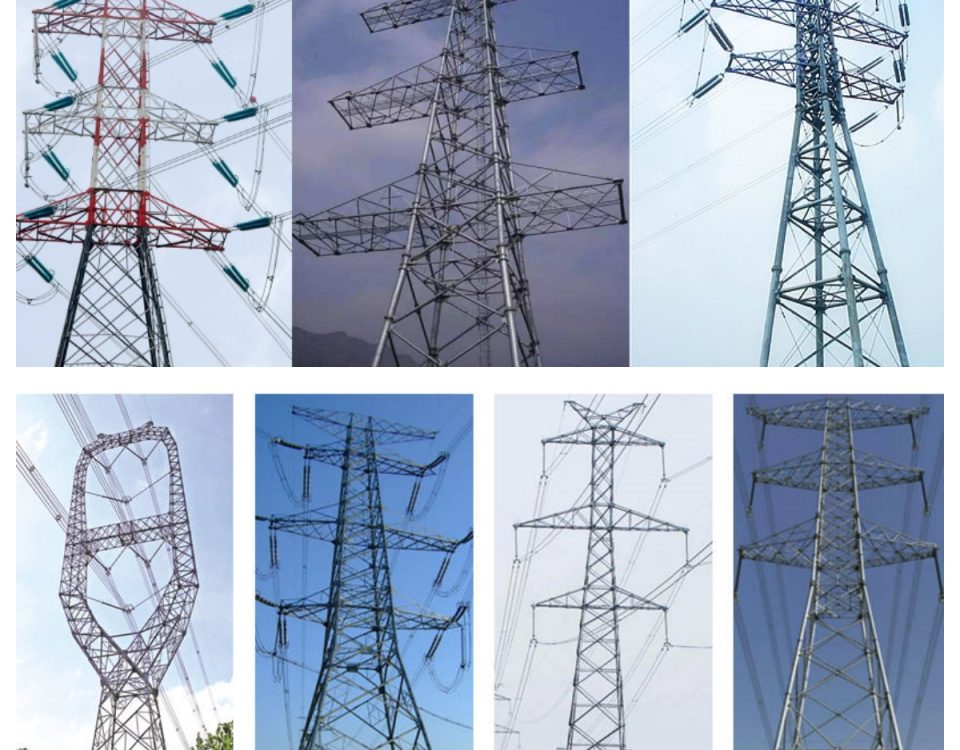
Transmission structures are one of the most visible elements of the electric transmission system. They support the conductors
used to transport electric power from generation sources to customer load. Transmission lines carry electricity over long
distances at high voltages, typically between 115 kV and 765 kV (115,000 volts and 765,000 volts).
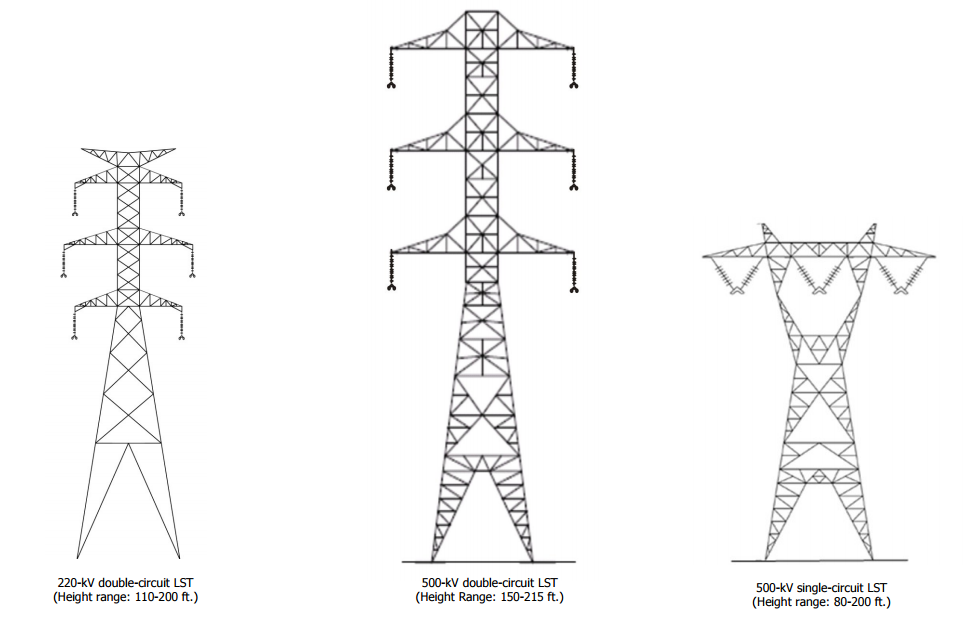
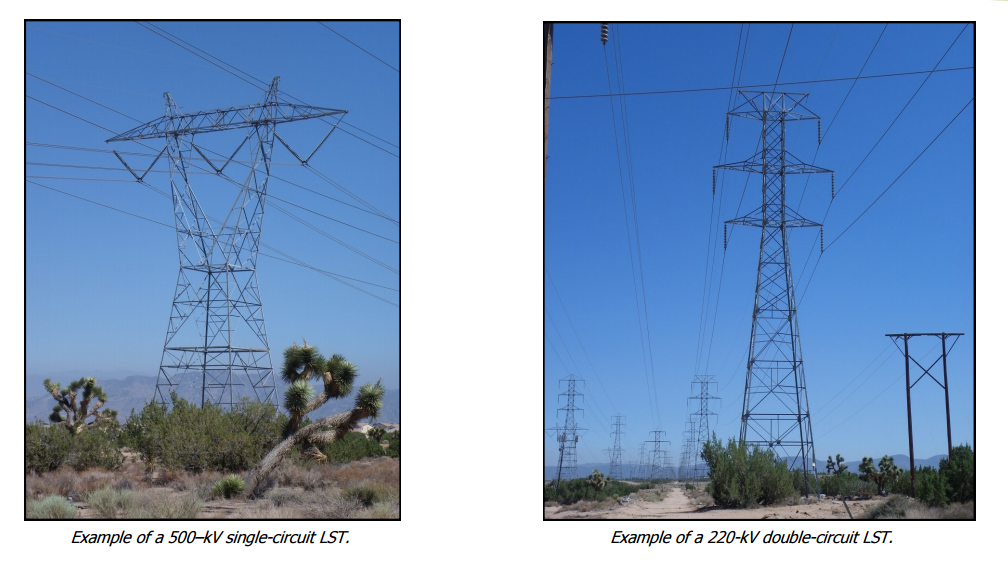
There are many different designs for transmission structures. Two common types are:
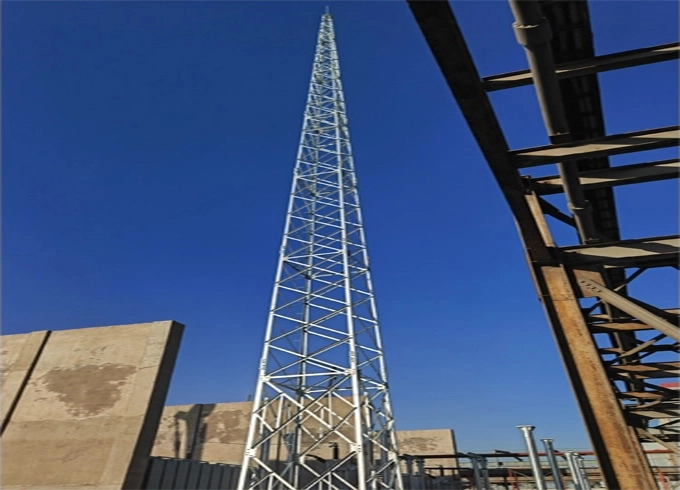
Lattice Steel Towers (LST), which consist of a steel framework of individual structural components that are bolted or welded together
Tubular Steel Poles (TSP), which are hollow steel poles fabricated either as one piece or as several pieces fitted together.
The foundation part of the structure is placed within the foundation excavation, it is centred and fixed, and then the concrete is cast in the foundations. Further assembly is made after the concrete solidifies. The structure can be mounted element by element (one element at the time), in parts (sections) or in one piece (complete).
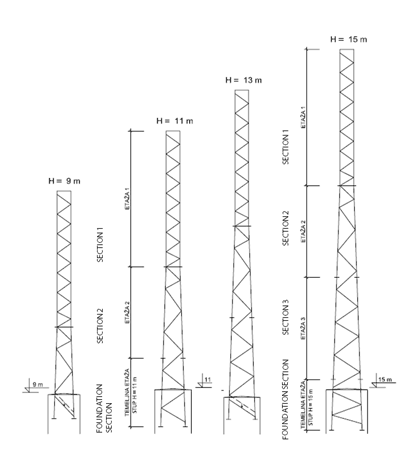
Sections of the towers are composed of main legs of max. length 6m connected with diagonals, and the same section is used for towers of different heights without requiring additional works on the structure as such. In this way the storage (number of positions) and assembly of towers is simplified. It makes possible to very simply use them on different locations in case the existing tower is to be disassembled, as also makes possible to use then for lower heights, that is the foundation section can be used for both equal and for higher towers.













