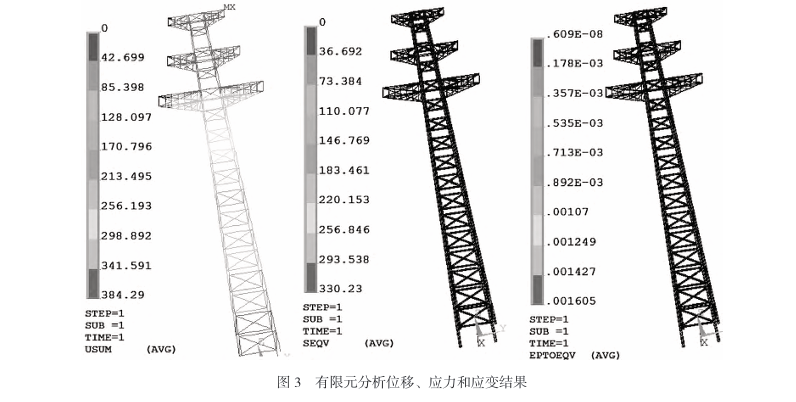
Exploration of Smart Manufacturing Applications in Transmission Tower Production
March 18, 2025
Forest Fire Prevention Monitoring Communication Towers
March 25, 2025Cost-Saving Strategies in Transmission Tower Manufacturing
Cost-Saving Strategies in Transmission Tower Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Analysis
The global transmission tower market, valued at $15 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.11% to reach $18 billion by 2030 (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%202). With increasing demand for electricity, aging infrastructure replacement, and geopolitical shifts in manufacturing, tower manufacturers face intense pressure to optimize production costs while maintaining quality and compliance. This report explores actionable strategies for cost reduction across material selection, advanced manufacturing, energy efficiency, supply chain management, automation, and quality control, supported by case studies and industry benchmarks.
1. Material Optimization: Balancing Strength, Weight, and Cost
1.1 Aluminum Adoption for Structural Components
Aluminum’s conductivity (61% of copper) and lightweight properties make it ideal for reducing tower weight without compromising structural integrity. For example, replacing steel components with aluminum alloys can decrease the load on foundations and support structures, lowering transportation and installation costs by up to 15% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%206). Tata Power’s 110 kV “narrow tower” design exemplifies this approach, reducing land footprint by 30% while maintaining safety standards (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%201).
1.2 High-Strength Steel and Design Innovations
Using S355 medium-strength steel for tower legs and cross-arms optimizes cost-to-strength ratios. Research shows that reducing material thickness while increasing component count can lower steel usage by 10–15% without sacrificing structural performance (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2011). For instance, Bonneville Power Administration’s Advanced Tower Analysis and Design Software reduced steel requirements by 20–35% per tower, saving 18,000–18,000–270,000 per unit (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2042).
1.3 Composite Materials in Niche Applications
Fiber-reinforced polymers (FRPs) are gaining traction for insulators and cross-arms in corrosive environments. While FRPs are 20–30% costlier than steel, their resistance to weathering reduces maintenance costs by 40% over a tower’s 50-year lifespan (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2014).
2. Advanced Manufacturing Technologies
2.1 Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
3D printing enables complex geometries, reducing material waste by 25–30% compared to traditional casting. For small-batch components like custom brackets, additive manufacturing cuts tooling costs by 60% and lead times by 50% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2018). Voortman Steel’s automated welding systems integrate 3D-printed jigs, improving weld accuracy and reducing rework costs (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2034).
2.2 Robotics and AI-Driven Automation
- Welding Robots: Automated welding systems achieve 99.5% consistency in joint quality, reducing defects by 70% and labor costs by 40% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2032).
- Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms analyze sensor data from CNC machines, predicting failures 48 hours in advance and lowering downtime costs by 25% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2016).
2.3 Industrial IoT and Digital Twins
Real-time monitoring of production lines through IoT sensors optimizes energy consumption and material flow. For example, Ansteel’s smart supply chain platform reduced logistics costs by ¥2.3 billion ($320 million) over three years by synchronizing raw material deliveries with production schedules (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2026).
3. Energy Efficiency in Production Processes
3.1 Process Optimization
- Waste Heat Recovery: Capturing heat from galvanizing furnaces to preheat raw steel slabs reduces energy consumption by 15–20% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2023).
- Renewable Integration: Solar microgrids at Nanjing Daji’s factory cover 30% of energy needs, saving $120,000 annually in electricity costs (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2024).
3.2 Lean Manufacturing Principles
By adopting value-stream mapping, KEC International reduced idle time in its cutting and drilling lines by 18%, boosting annual output by 12% without capital expenditure (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2024).
4. Supply Chain and Logistics Optimization
4.1 Regionalized Procurement
Shifting from global to regional suppliers (e.g., sourcing steel from Vietnam instead of China) lowers tariffs and transportation costs by 8–12%. The U.S.-Mexico manufacturing corridor has reduced lead times for North American projects by 20% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%201).
4.2 Collaborative Supplier Networks
Ansteel’s partnership with developed reusable containers for coal transport, cutting losses from (bulk-to-container) operations by 45% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2026).
5. Automation in Structural Fabrication
5.1 Integrated Production Lines
Zhejiang Shengda’s fully automated line integrates laser cutting, robotic welding, and AI-based quality inspection, achieving a production rate of 120 tons/day with 30% fewer workers (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2033).
5.2 Modular Design and Prefabrication
Prefabricating tower sections in factories reduces on-site labor by 50% and accelerates project timelines. For example,分片式 (segmented) concrete towers lowered installation costs by 18% in low-wind regions (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2012).
6. Environmental Compliance and Cost Management
6.1 Circular Economy Practices
Recycling 85% of steel scrap from cutting operations saves 80–80–100/ton in raw material costs. Ansteel’s closed-loop system recovers 12,000 tons of scrap annually, reducing carbon emissions by 8,400 tons (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2026).
6.2 Emission-Reduction Technologies
Instulating electrostatic precipitators in coating booths reduces VOC emissions by 90%, avoiding 50,000–50,000–100,000 in annual fines (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2036).
7. Competitor Benchmarking and Cost Leadership
7.1 Lightweight Design Leadership
Tata Power’s towers use 18% less steel than industry averages through topology optimization, achieving a 22% cost advantage in urban projects (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%201).
7.2 Vertical Integration
Kalpataru Power’s in-house galvanizing facilities save 150–150–200/ton compared to outsourcing, translating to 5–7% lower total project costs (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%205).
8. Quality Control Systems for Cost Containment
8.1 Automated Inspection Systems
Machine vision systems detect weld defects with 99.8% accuracy, reducing rework costs by 60% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2046).
8.2 Predictive Quality Analytics
By correlating material hardness data with field failure rates, Prysmian S.p.A. adjusted heat treatment parameters, lowering warranty claims by 35% (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%2048).
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Cost Reduction
Transmission tower manufacturers must adopt a multi-pronged strategy to remain competitive:
- Prioritize material innovation (e.g., aluminum alloys, composites) to reduce weight and logistics costs.
- Invest in Industry 4.0 technologies (robotics, IoT, AI) to optimize energy use and minimize defects.
- Regionalize supply chains and collaborate with stakeholders to mitigate geopolitical risks.
- Implement circular economy practices to align with environmental regulations while lowering costs.
Companies like Tata Power, Ansteel, and Voortman Steel demonstrate that integrating these strategies can achieve 20–30% overall cost reduction while supporting global energy transition goals. As the market grows to $18 billion by 2030 (app://obsidian.md/Evidence%202), manufacturers that balance innovation with operational efficiency will dominate the next decade of infrastructure development.
Related posts
The analysis of the bearing capacity of a power transmission line steel tower highlights the complexity and importance of structural and foundation design. By understanding the interplay of loads, material properties, and environmental factors, engineers can optimize tower performance and ensure reliability in power networks. Tables and case studies further illustrate best practices and design considerations.