The application and the history of steel
April 16, 2018
Corrosion and Protection of Transmission Steel Structure Tower
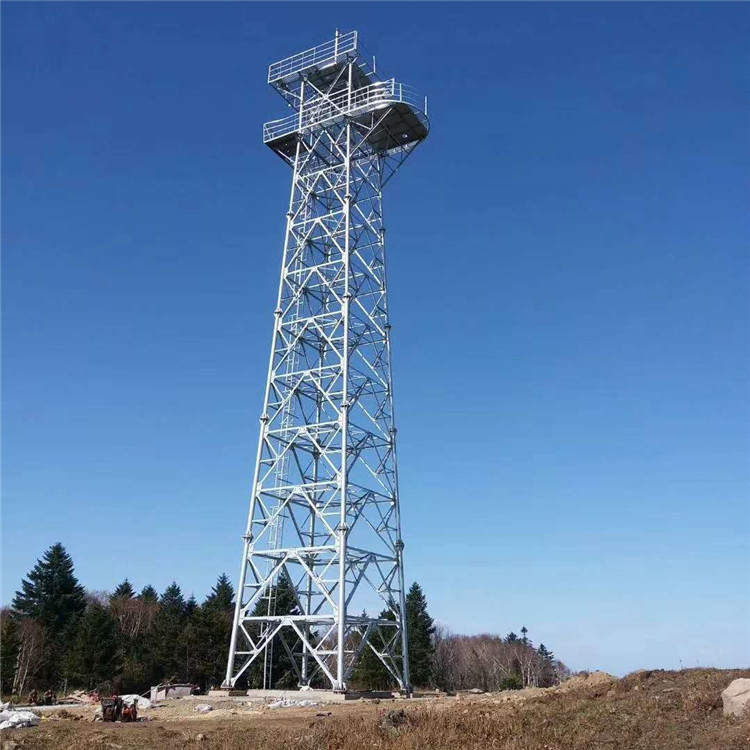
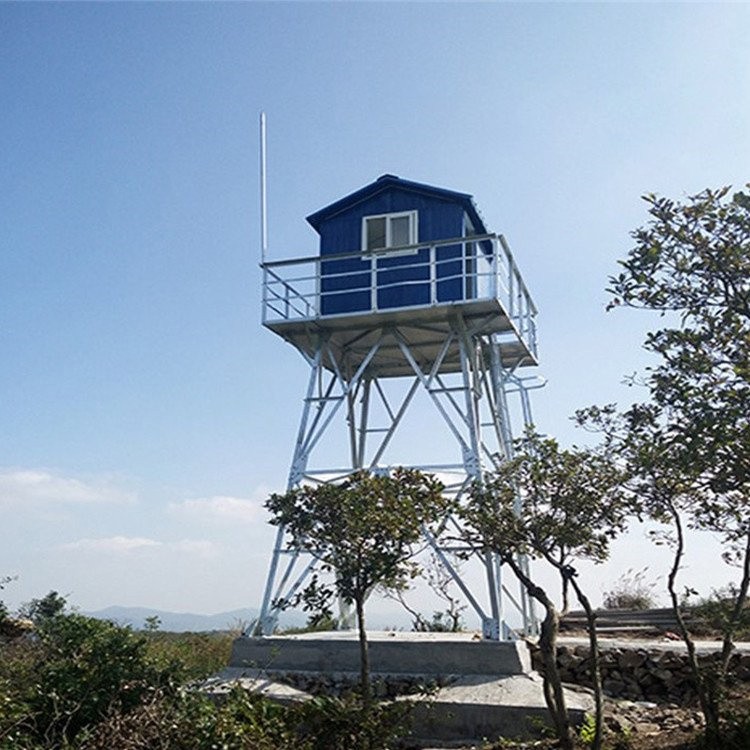
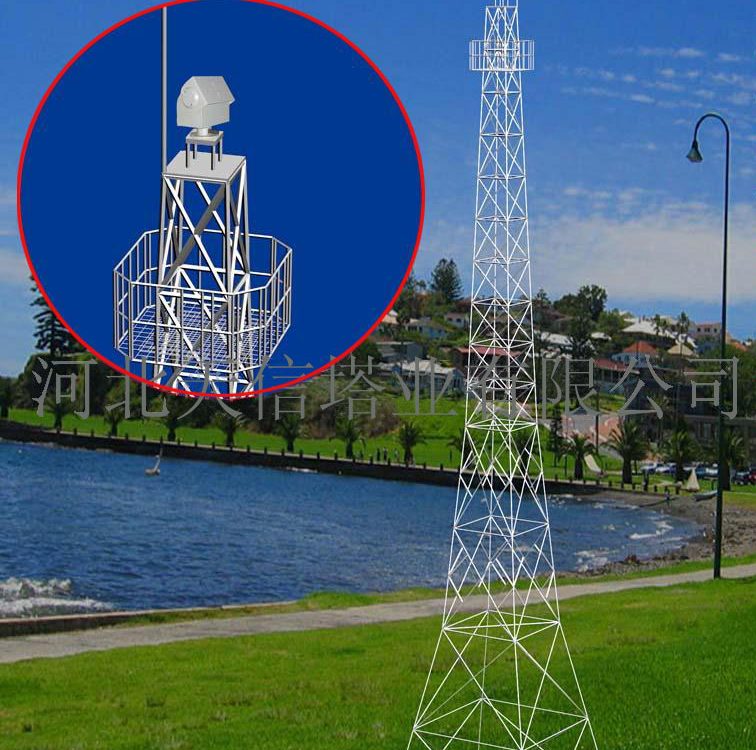
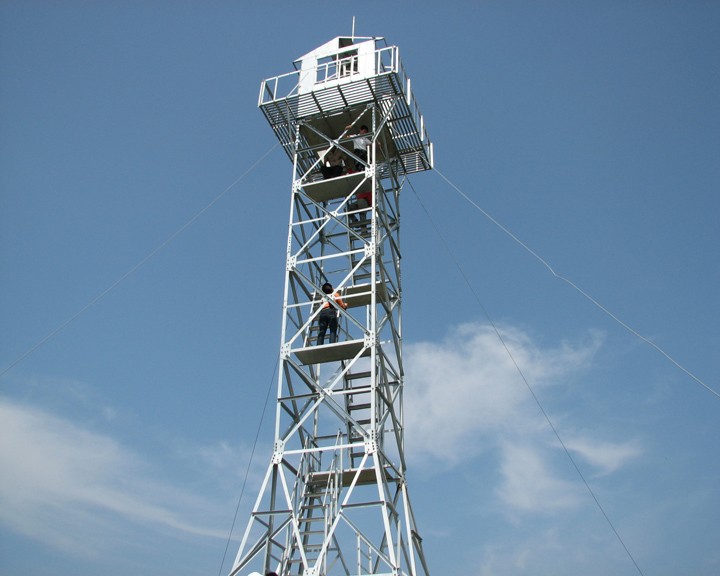
April 17, 2018Fire lookout tower, Standard Lookout Steel Structure For Forest Service
What is a fire lookout tower?
Fire lookout Tower plays an important role in forest fire detection, which can be used to report the forest fire in a timely manner, and watchtower can be a tourist attraction.
A fire lookout tower, fire tower or fire watchtower, provides housing and protection for a person known as a “fire lookout” whose duty it is to search for wildfires in the wilderness.
1, in the mountains to build two fire watchtower, you can look to the whole mountain, and stand high, looking far, eliminate lookout blind area, can save a lot of manpower.
2, with a fixed fire lookout tower, Indoor Lookout, Ranger on the one hand can be free from the sun and the sun, suffering from the cold, on the other hand can focus on forest fires.The construction of Fire lookout tower will better embody the guideline of forest fire prevention, and ensure the safety of people’s life and property, and protect the forest resources in mountainous area.

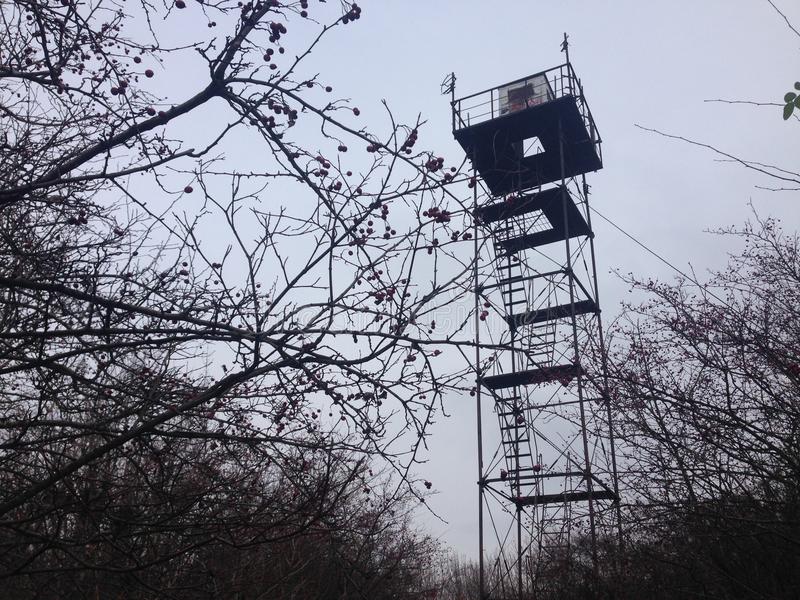
Lookouts: A lonely but honorable job
Like many lookout towers still standing in federally protected forests, the fire towers of Lincoln National Forest were built during the early and mid-1930s — the height of the Great Depression — by members of the Civilian Conservation Corps, President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal work relief program for young, unemployed men and World War I veterans. Alongside roads, trails, bridges and park facilities, the Conservation Corps built hundreds upon hundreds of fire towers during this period.
Fire spotter Janice Mackey, 1956The building of these far-flung fire towers didn’t just generate construction jobs. From the 1930s onward, the U.S. Forest Service enlisted hundreds of trained fire tower operators, many of them women. Acting as a tower-bound sentinel deep in a forest or atop a mountain was a lonely and thankless task, but these paid lookouts took pride in their work — particularly during the heyday of Smokey Bear when forest fire prevention was, well, trendy.
Hot-dip galvanizing Fire lookout tower Product Description
All towers are engineered and fabricated in accordance with the IBC (International Building Code) to meet the specific wind and seismic requirements of the project location.
Structural members and tower components (handrails, stairs, bracing, platform) are fabricated, then painted or galvanized, and ship with detailed instructions for ease of assembly. All hardware and fasteners are included for field assembly on site.
All structural members and tower components bolt together and no cutting or field welding is required for assembly.

|
Design |
||
|
1. Design Code |
TIA/EIA-222-G/F |
|
|
Structure Steel |
||
|
2. Grade |
Mild Steel |
High Tensile Steel |
|
GB/T 700:Q235B, Q235C,Q235D |
GB/T1591:Q345B, Q345C,Q3455D |
|
|
ASTM A36 |
ASTM A572 Gr50 |
|
|
EN10025: S235JR, S235J0,S235J2 |
EN10025: S355JR, S355J0,S355J2 |
|
|
3. Design Wind Speed |
Up to 250 km/h |
|
|
4. Allowable deflection |
0.5 ~1.0 degree @ operational speed |
|
|
5. Tension strength (Mpa) |
360~510 |
470~630 |
|
6. Yield strength (t≤16mm) (Mpa) |
355 |
235 |
|
7. Elongation (%) |
20 |
24 |
|
8. Impact strength KV (J) |
27(20°C)—Q235B(S235JR) |
27(20°C)—Q345B(S355JR) |
|
27(0°C)—Q235C(S235J0) |
27(0°C)—Q345C(S355J0) |
|
|
27(-20°C)—Q235D(S235J2) |
27(-20°C)—Q345D(S355J2) |
|
|
Bolts & Nuts |
||
|
9. Grade |
Grade 4.8, 6.8, 8.8 |
|
|
10. Standards for mechanical properties |
||
|
10.1 Bolts |
ISO 898-1 |
|
|
10.2 Nuts |
ISO 898-2 |
|
|
10.3 Washers |
ISO 6507-1 |
|
|
11. Standards for Dimensions |
||
|
11.1 Bolts |
DIN7990, DIN931, DIN933 |
|
|
11.2 Nuts |
ISO4032, ISO4034 |
|
|
11.3 Washers |
DIN7989, DIN127B, ISO7091 |
|
|
Welding |
||
|
12. Method |
CO2 Shielded Arc Welding & Submerged Arc Welding(SAW) |
|
|
13. Standard |
AWS D1.1 |
|
|
Marking |
||
|
14. Method of marking of the members |
Hydraulic Press Stamping |
|
|
Galvanizing |
||
|
15. Galvanization standard of steel sections |
ISO 1461 or ASTM A123 |
|
|
16. Galvanization standard of bolts and nuts |
ISO 1461 or ASTM A153 |
|
|
Test |
||
|
17. Factory test |
Tensile test,Elements analysis, Sharpy test(impact test), Cold Bending, |
|
|
Capacity |
||
|
18. Maximum Production Capacity |
50,000 TON per annum |
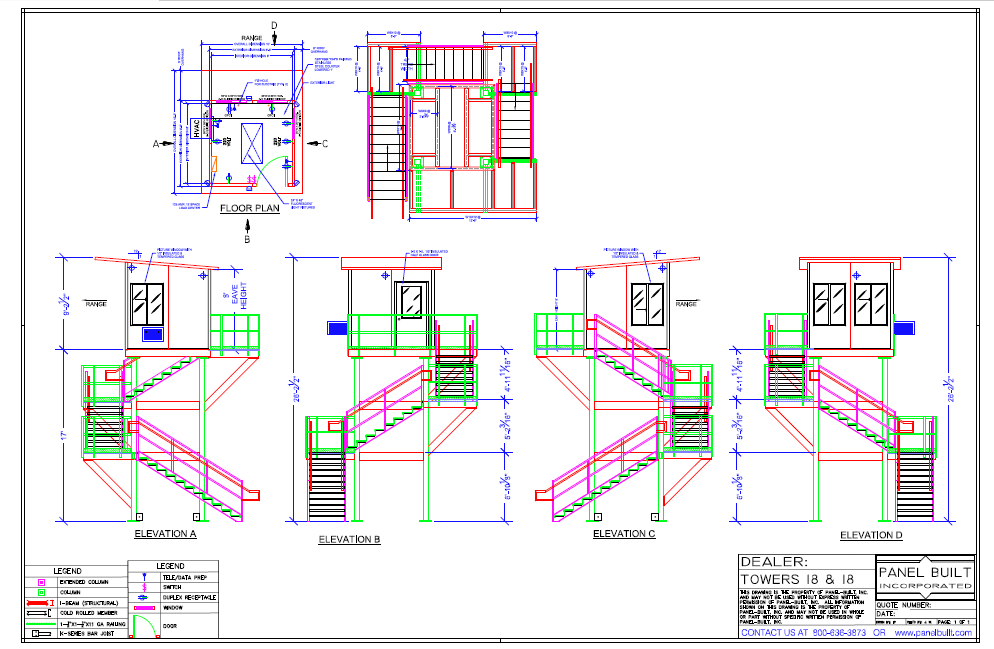
|
Fire lookout Steel Tower CAD









