Monopole Telecommunication Tower Design Code,Type and Installation
April 28, 2018Transmission tower project map in Africa
May 2, 2018Self-supporting Communication Tower Design Standards & Mechanical properties
Tower Design STANDARDS & CODES
Design of the towers shall comply with British Standard (BS) 5950. These shall cover the following:
Self-supporting Communication Tower Foundation
- Foundation reinforcement should comply with British Standard (BS) 4449. The minimum grade of concrete shall be C30 as per British Standard (BS) 8110.
- to either provide “soil investigation report” or define the characteristics of the soil by specifying the “soil bearing capacity”.
Contractor is obliged to provide the foundation design for approval based on the supplied information.The foundation shall be designed for each site specifically & the site specific foundation design shall be submitted to for approval prior to the commencement of the civil works at sites.
- Design and construction of foundations for the different height of the towers shall be for any type of soil or rock conditions. The foundation to be designed as per recommendations of Omantel or soil investigation report and relevant ACI code. No additional amount will be entertained for the excavation in rock, cemented gravel, etc.
- The contractor is solely responsible for the structural stability of the supplied Self-supporting Communication Towers in all aspects and approval does not release the contractor from the responsibility for any unfortunate contingent adverse occurrence in the future.
- To ensure quick curing of the foundation concrete, the contractor is obliged to utilize proper curing compounds. The contractor shall seek approval for the curing compounds that are going to be utilized.
- Epoxy coated reinforcement steel shall be utilized for the sites within 2km range from the sea.
- All tests required including cylinder test, pile integrity test, concrete core test (in case of unsatisfactory cylinder test results) etc. shall be carried out for all piles / foundations.
- Non-shrink cementatious grout “CONBEXTRA GP” or equivalent to be placed below the base plates of the Communication Towers legs. (Minimum thickness 50mm).
- The concrete surface below ground level shall be protected by two coats of approved bituminous coating ‘NITACOAT ET550’ or equivalent. Above ground level, the concrete surface shall be protected by crack accommodating elastomearic protective coating topcoat “DECKGUARD E2000” or equivalent.
- All foundation work including excavation and backfilling shall be carried out as per relevant ASTM standard. The reinforcement steel should be as per the relevant British Standards.

Steel Grade & Steel Elements
- All structural angle sections, plates and other sections shall comply with relevant British Standards.
- Sections used in the fabrication of members shall be cut from single piece of material (no welded pieces).
- Grades of the steel to comply with BS EN 10025 Grade 275 JR/355 JR or equivalent ASTM
- Materials used in production of steel work shall be provided free from blisters, mill scale, laminations and other defects.
- The minimum yield and tensile strength of steel to be used for manufacture of steel work will be in accordance with the design calculations.
- Tower legs to be high grade steel and manufacturer shall identify clearly the grades of the steel in writing to the Employer.
- The necessary holes needed for the ground connection on the tower legs close to the base plates must be designed & drilled prior to galvanizing.
- Member usage allowed is maximum 85% in comp & Tension
- climatic conditions should be considered while designing the Self-supporting Telecommunication Towers .
Temperature degreeC, High Humidity climate , Exposed to Sand storm
Tower Heights
Heights of Square self support towers shall be in an increment of 5 meters(i.e. 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60, 65,70, 80 & 90m.
Heights of Triangular self support towers shall be in an increment of 5 meters(i.e. 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55 & 60m
If specific site conditions demand deviation from the above-mentioned height increment, detailed technical justification must be specified.
The towers shall be designed for at least for a life time of 30 years.
Definition of Wind Speed
Since the wind force on a structure depends on the square of the wind speed, the specification of wind speed is critical in determining the weight, rigidity, and cost of a mast or tower. Every effort should be made to specify the realistic maximum wind speed for the location based on a 3 second gust value.
There are two wind speeds which are important for the design: the maximum wind speed in which twist and sway shall be maintained within the specified limits (operational wind speed); and the survival wind speed in which the twist and sway specification shall be temporarily exceeded during extreme gusts but the structure shall return to normal afterwards. These correspond to the 10 and 50 year maximums, respectively. In this case, the towers shall be capable of sustaining survival wind speed of 55.56 m/sec or 200 km/h at 3 second gusting and the operational wind speed shall be 44.44 m/sec or 160 km/h.
Wind Pressure (Loads)
The wind load on a Self-supporting Communication Towers or mast is the combined effect of the wind pressure on its structural components and on the antennas which it supports. Antenna manufacturers will normally indicate the wind load for their products at an indicated wind speed. A grid has approximately 65 to 70% less exposed area than a solid dish of the same diameter whilst a Radom fitted to a solid dish improves the dynamic wind flow and hence reduces wind pressure.
The contractor is responsible for combining the total load and for any recalculation of the antenna load at the specified wind speed according to the antenna loading criteria for the structure. Wind pressure on the structural members, ladders, antenna mounts, etc. shall be calculated in accordance with British Standard (BS) 8100 on open areas without obstruction.
Consider Topography category 2 with minimum 10 mt crest height.
Expose category D as per ANSI / TIA / EIA / RS -222-G
Factored load should be considered at survival wind speed for Design check
Twist & Sway
All structures move in the wind to some extent. The directivity of the antennas shall determine the allowable twist and sway. In the absence of specific requirements it is normal to limit these values to ±0.5 degrees which should give adequate performance of most radio systems under extreme wind conditions.
Twisting of guyed masts can be reduced by using spreader bars or anti-torque devices between the mast structure and the upper end of the guy wires.
Related posts
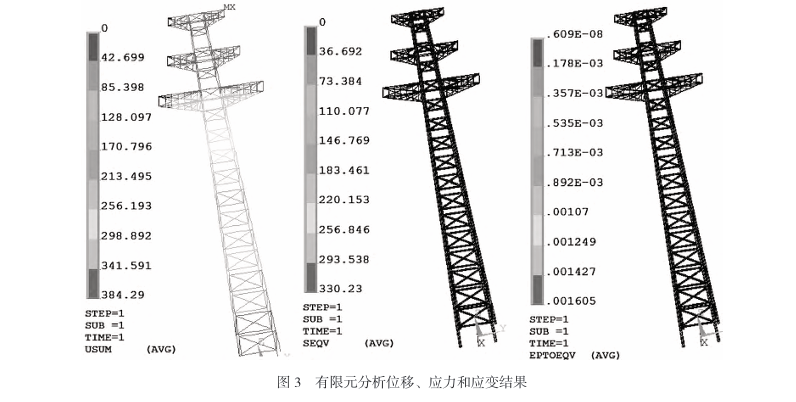
The analysis of the bearing capacity of a power transmission line steel tower highlights the complexity and importance of structural and foundation design. By understanding the interplay of loads, material properties, and environmental factors, engineers can optimize tower performance and ensure reliability in power networks. Tables and case studies further illustrate best practices and design considerations.