Microwave Communication Steel Tower Manufacturer & Installer
April 23, 2018
double circuit transmission tower manufacturer – Stronger Steel Tower
April 24, 2018What type of cell phone communication tower ? How to Building Tower?
FIVE MAIN TYPES OF TOWERS
Cell phone communication towers are an essential part of providing Cell phone communication service. A collection of Cell phone communication towers creates a cellular network, which provides coverage to a large region. Cell phone communication companies are frequently looking to build new Cell phone communication towers in order to strengthen their service in a particular area, and these companies are often willing to rent already built Cell phone communication towers on private property. Thus, if you have the means, building a Cell phone communication tower on your property can be very profitable.
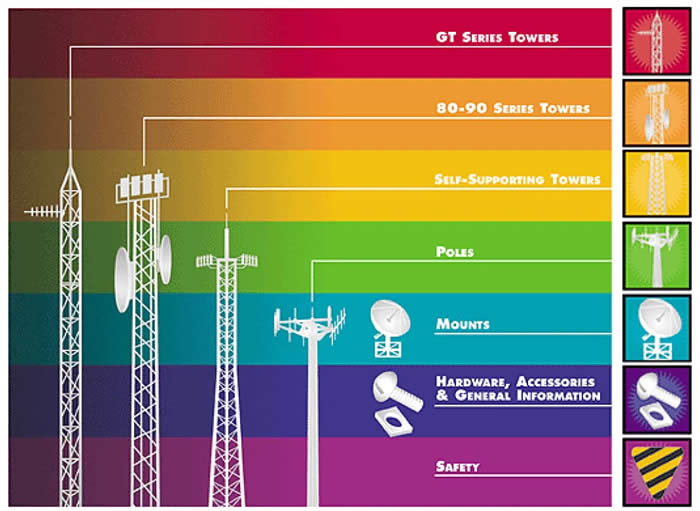
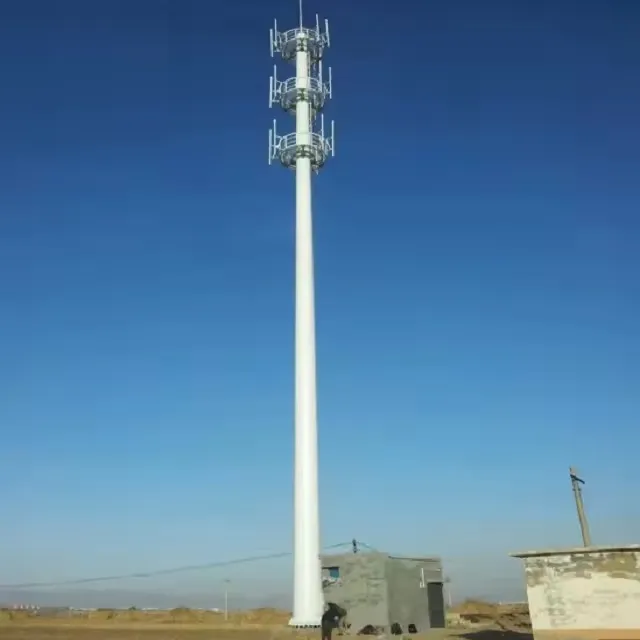
The Monopole Tower is a single tube tower. It typically stands between 100-200 ft. with antennas mounted on the exterior of the tower. Its primary use is telephony.
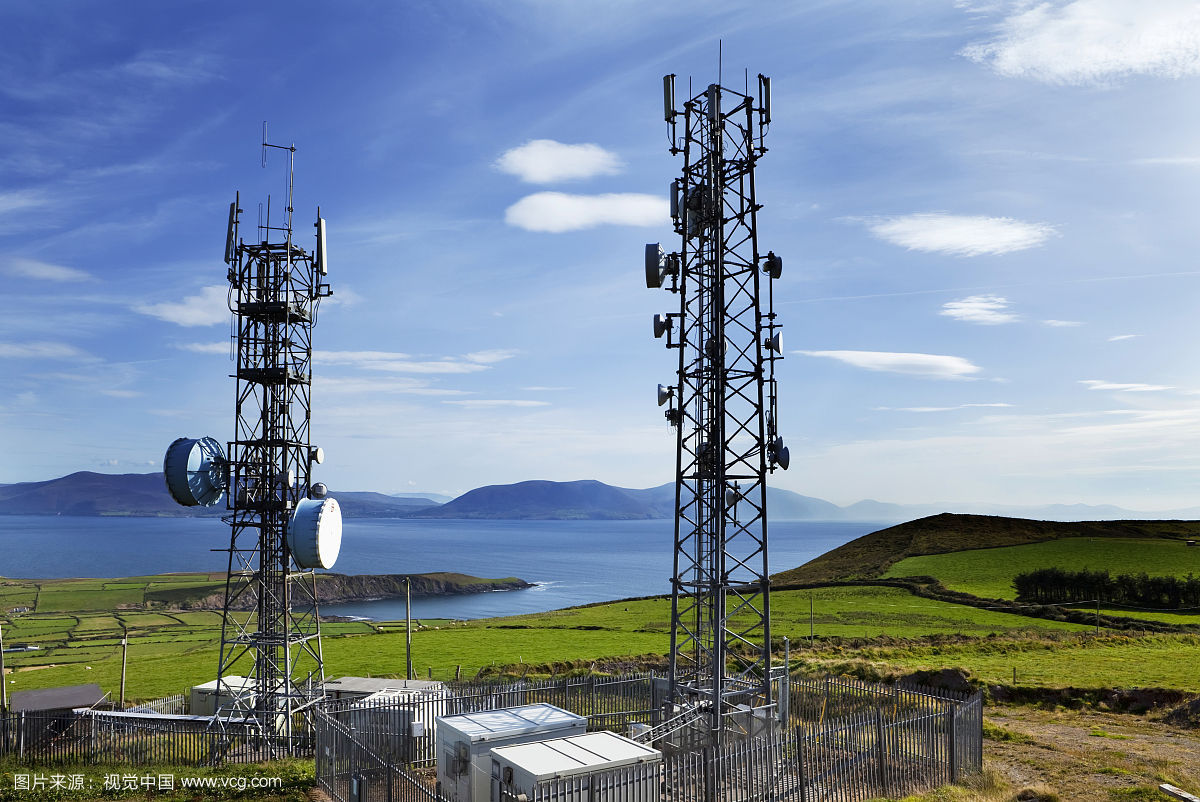
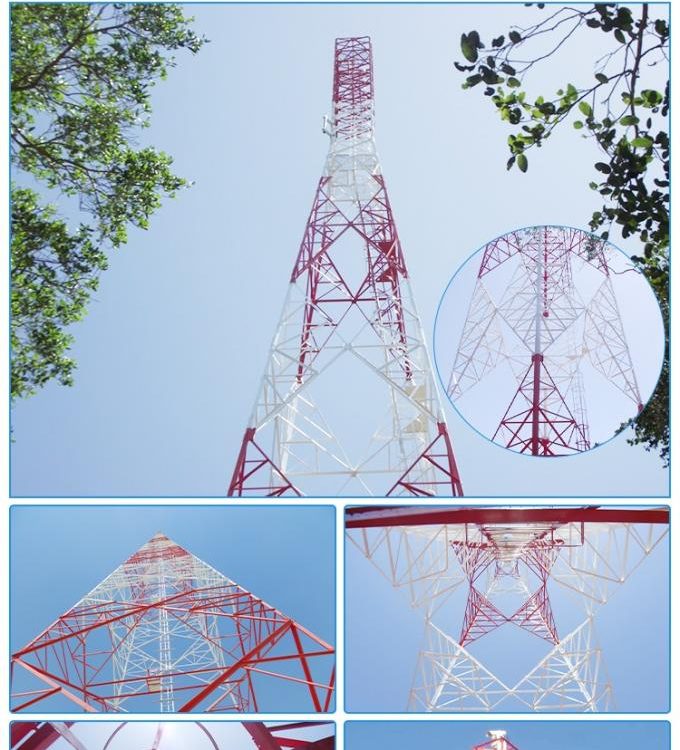
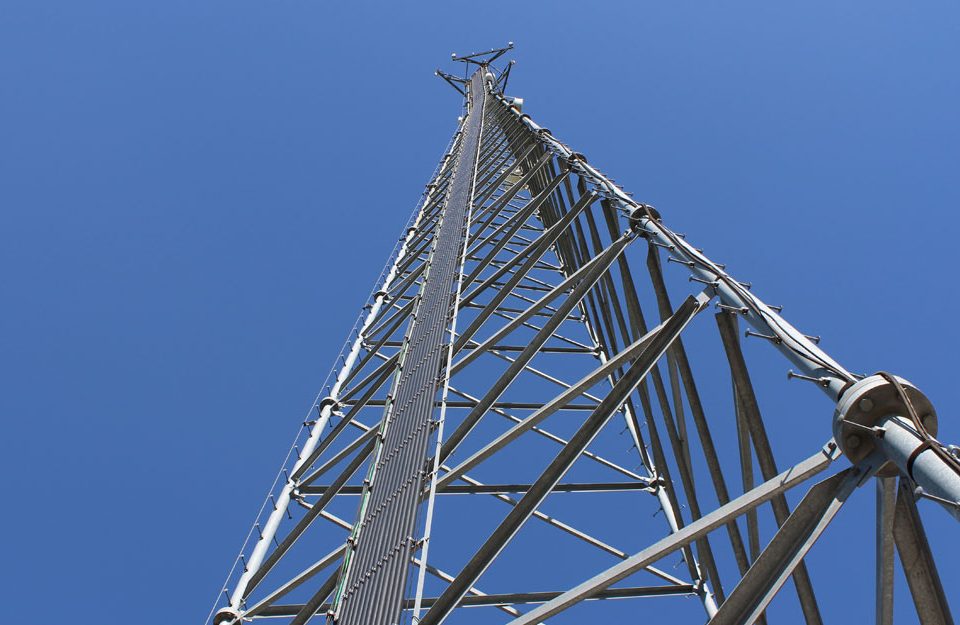
The Lattice Tower A lattice tower is often called a self-supporting tower. Lattice towers are generally made out of steel and offer the most stability of the cell phone tower types. A lattice tower can be found in either a square or a triangular shape. The lattice towers offer the most flexibility of all of the cell tower types.
The Guyed Tower is basically a straight rod supported by wires that attach to the ground as support. It’s cheapest to construct, especially at heights of 300 ft and beyond. Some guyed towers reach as high as 2,000 ft. Typical uses are: telephony, radio, television, and paging.
Concealed Towers Concealed Tower are a particular brand of concealed towers. Another manufacture of concealed towers in Larson Camouflage. Concealed towers are deployed to satisfy zoning regulations, and can range in size to accommodate their surroundings. They are more expensive than other types of towers because they require additional material to create a “concealed appearance,” yet at the same time, they provide less capacity to tenants than other towers do. Below is one of the more interesting concealed towers, located at a church in California.
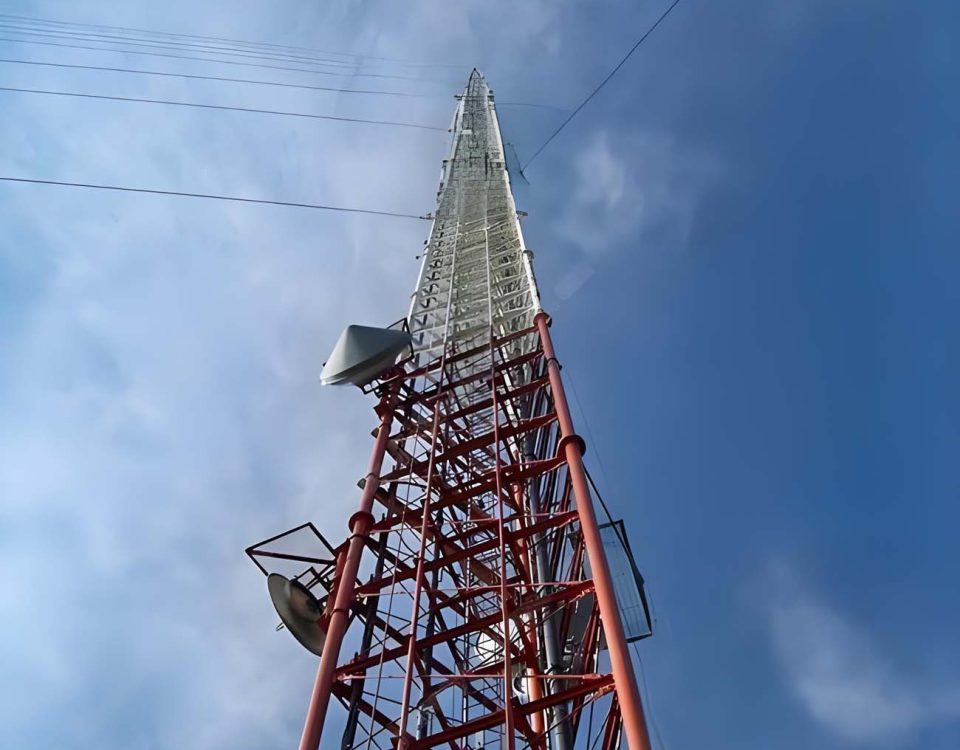
Broadcast Towers provide mounting space for FM radio, AM radio, and Television (TV) antennas. Their antennas are massive, weighing anywhere from 1,000 pounds to 15 tons depending upon the type of service they provide and the coverage they are purposed to deploy. Most broadcast towers are guyed towers with three or more guy wires attached to grounded anchors. Broadcast towers can take up a great deal of ground space – up to 300 acres, which is why they are typically found in rural areas or on mountaintops where natural elevation provides the best means of transmitting signals.
Cell phone communication towers are structures built on specific parcels of land that are designed to accommodate wireless tenants. Wireless tenants utilize cell towers to deploy various technologies to a subscriber base, such as telephony, mobile data, television and radio. Cell towers are typically built by tower companies or wireless carriers.
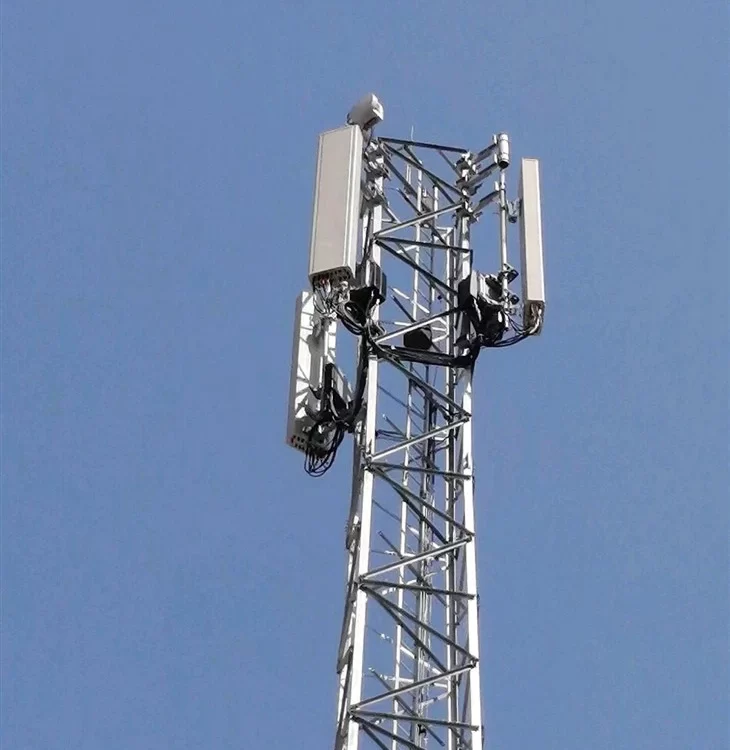
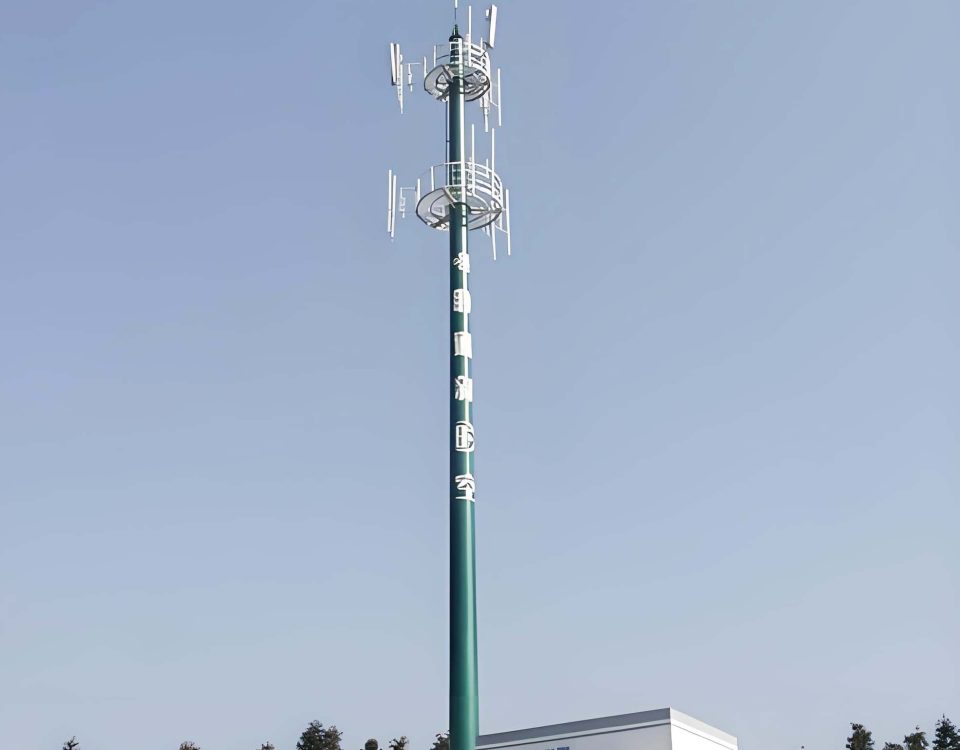
An Antenna Array is a platform where tenants mount antennas, which signal transmission and reception to mobile devices within a specific area. The number of antennas (typically between 3-18) is based on several factors, including the number of tenants (wireless carriers); the type (voice or data) and volume of transmission; the technology being used (eg: CDMA, GSM, LTE, WiMAX) and the frequency of spectrum (in MgH) utilized.
microwave dish
The Microwave Dish is a large round antenna, which is used for a specific type of transmission, and also commonly used for backhaul.
cell tower ground lease
The Ground Space is the area that wireless carriers lease from property owners, upon which they build cell towers, cell sites and place shelters, generators and additional equipment.
Base Transmitter Station
The Base Transmitter Station or BTS is a shelter or enclosed area used to house and protect communications, radio and network equipment.
The Generator is powered by gas or diesel and used as emergency back-up to keep cell sites operational during power outages.
Utilities are also necessary for the operation of cell sites. Wireless carriers will run lines or cables to the site to complement their specific technology.

Building a Cell phone communication tower
Building a Cell phone communication tower requires money, permission and outside workers.
Step1
Obtain good land. The most important aspect of being able to build a Cell phone communication tower is to have good land to build it on. Ideal land for the construction of a new Cell phone communication tower includes being far away from other towers, being in a densely populated area that uses cell phones and being in an area that your local government has zoned for the building of a Cell phone communication tower.
Step2
Find an interested Cell phone communication company. Building a Cell phone communication tower can be very expensive (upward of $318,000). Thus, you don’t want to build one unless you know a Cell phone communication company is interested in leasing your tower. Many local governments won’t even allow you to build a Cell phone communication tower unless you have a letter of intent from an interested Cell phone communication company.
Step3
Contract workers. Needless to say, the construction of a Cell phone communication tower is not an activity that can be done by a single person. While there are several different types of towers, the construction workers will build a tower that includes four basic parts: the tower itself, equipment, antennas and utilities.
We receive many inquiries from property owners who confuse the actual tower with antennas that are placed on rooftops. These antennas are more accurately described as cell “sites”, but the real definition of a cell site is: an area within a wireless service providers network that can be serviced by an antenna array. Thus, there can be multiple cell sites (and multiple tenants) on any one given tower (or rooftop). This article will help clarify the difference between the types of towers and the equipment that is placed on and used for cell site transmissions.










